Gambling is a common activity among adolescents. Most adolescents gamble without consequences but some experience gambling-related problems and associated harms, including disrupted social relationships, academic challenges, delinquency, and criminal behavior. Their gambling behavior might be influenced by the gambling attitudes and behaviors of their family and friends. This week, The WAGER reviews a study by Megan Freund and colleagues that investigated whether exposure to other people’s gambling is associated with the gambling behavior of Australian secondary students.
What was the research question?
Is exposure to other people’s gambling associated with past-month gambling, types of gambling activities, and at-risk or problem gambling among a sample of Australian adolescents?
What did the researchers do?
Students (n = 6,377) from 93 secondary schools in the Australian states of Victoria and Queensland participated in the Australian Secondary Students’ Alcohol and Drug Survey. Participants reported whether they had ever gambled and their past-month gambling behaviors, including the types of gambling activities they engaged in (i.e., hard or soft1). Students who reported ever gambling were screened for problem gambling. Participants were also asked whether their parent/caregiver, brother/sister, best friend, or other relative had gambled in the past month. The researchers assessed the associations between other people’s gambling and students’ past-month gambling, types of gambling activities, and at-risk or problem gambling.
What did they find?
Thirty-one percent of students in the sample reported ever gambling and six percent had gambled in the past month. Ten percent of students who ever gambled were classified as either experiencing at-risk (8%) or problem gambling (2%). One in five students reported that someone in their household gambled in the past month. Most frequently, students reported past-month gambling among fathers (16%), followed by other relatives (14%). Students were more likely to have gambled in the past month, played any hard gambling activity, and be classified as an at-risk or problem gambler if they had a parent/caregiver, brother/sister, best friend, or other relative who had gambled in the past month. Past-month gambling and at-risk/problem gambling were most likely among students whose parent/caregiver or best friend had gambled (see Figure).
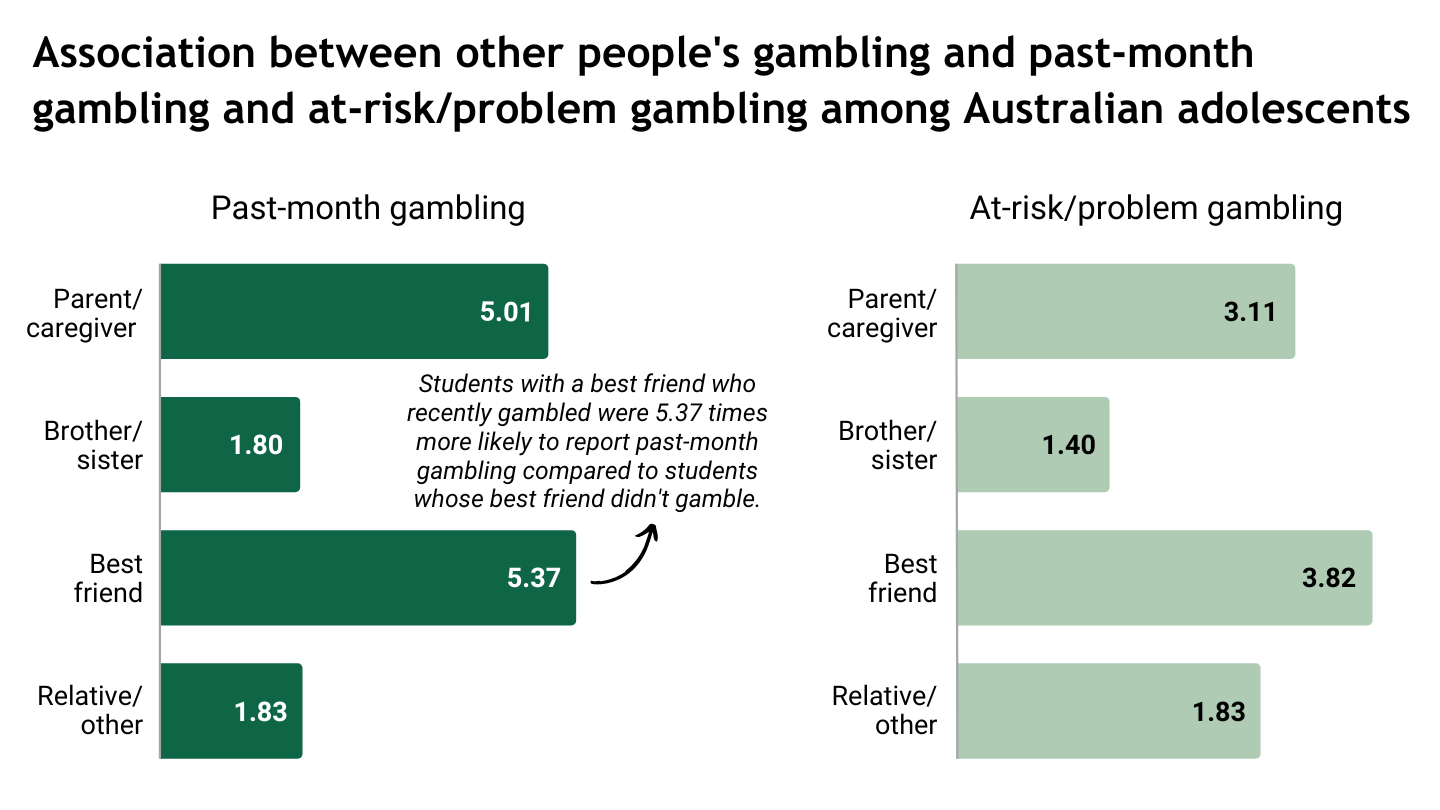
Figure. Odds ratios of the association between other people’s gambling (parent/caregiver, brother/sister, best friend, other relative/someone else) and past-month gambling and at-risk/problem gambling among a sample of Australian secondary students (n = 6,377). Click image to enlarge.
Why do these findings matter?
These findings confirm the association between exposure to gambling in family and friends and gambling behaviors among adolescents. Young people with a parent/caregiver or close friend who gambled were most likely to have gambled recently, engaged in hard gambling activities, and to have experienced at-risk or problem gambling. These findings should inform future problem gambling prevention and education initiatives for young people, such as family-focused initiatives. Successful initiatives might also include skill development for young people, such as how to resist peer pressure to gamble.
Every study has limitations. What are the limitations of this study?
Data were self-reported, so the results might be subject to recall bias and social desirability bias. Because the study was based on a sample of adolescents and was conducted in Australia, the findings might not be generalizable to people in other places with different gambling landscapes.
For more information:
Do you think you or someone you know has a gambling problem? Visit the National Council on Problem Gambling for screening tools and resources. For additional resources, including gambling and self-help tools, visit our Addiction Resources page.
— Kira Landauer, MPH
What do you think? Please use the comment link below to provide feedback on this article.
________________
1. Hard gambling activities are generally defined as having higher stakes or a more rapid pace of play (e.g., poker, casino games, sports betting) compared to soft gambling activities (e.g., lottery tickets, scratch cards).




