Social casino gaming is a booming industry; in 2016, revenues were estimated at $1,695 million in North America alone, mostly from advertising. In social casino gaming, no money is won or lost, but users play games that simulate casino games. In an effort to better understand characteristics of social casino gamers and inform responsible gaming protocols, Sally Gainsbury and colleagues compared social casino gamers with land-based casino gamblers. This week, The WAGER reviews this research.
What was the research question?
Among people who gamble, are those who play social casino games at particular risk for the developing gambling problems?
What did the researchers do?
Two thousand and ten Australian people who had gambled during the past year completed a telephone interview. They answered questions about their gambling and social gaming behavior, attitudes about gambling, problem gambling severity, substance use and mental health, and demographics. Gainsbury and colleagues divided the sample of past-year gamblers into two comparison groups: social casino gamers (n=270) and non-social casino gamers (n=1740).
What did they find?
Results suggest that problem gambling and other risky behaviors are strongly tied to social casino gaming. Compared to non-social casino gamers, social casino gamers were significantly more likely to fall into the low-risk (26.2%), moderate risk (14.8%), and problem gambler (4.7%) categories, and less likely to fall into the non-problem gambler category (54.3%). (See Figure) Social casino gamers were less likely to see harm in gambling. Additionally, social casino gamers were more likely to smoke everyday (32.3% compared to 13.6%) and reported higher levels of illicit drug use, which are both commonly comorbid with problematic gambling. Social casino gamers were more likely to be male, relatively young, and unmarried, and to have home Internet access.
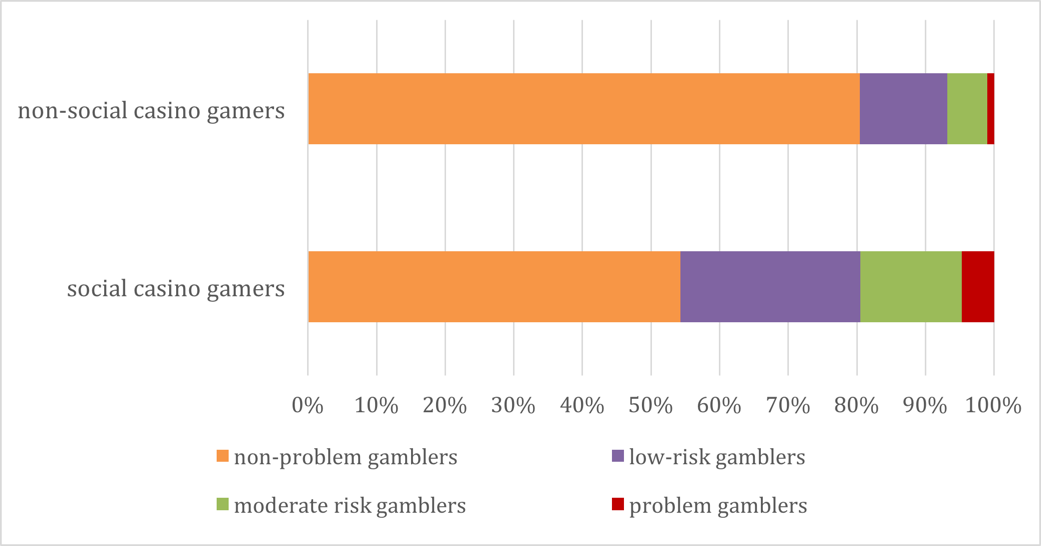
Figure. Problem Gambling Severity Index (PGSI) groups, comparing social casino gamers and non-social casino gamers. Click image to enlarge.
Why do these findings matter?
Throughout history, people have worried that new forms of technology will stimulate addictive tendencies, and the same is true of social casino gaming. Social casino gaming is a new market and relatively free of regulation. If it triggers gambling urges and encourages mistaken beliefs about gambling, it could be a dangerous activity. However, social casino gaming might simply attract people who are naturally at higher risk for gambling problems. This study’s findings indicate that we need to learn more about these players—what motivates them and how they might respond to regulation and prevention strategies.
Every study has limitations. What about this one?
This research did not measure psychological predictors, such as impulsivity, sensation-seeking, or risk-taking, which might emerge before social casino gaming and might provide more insight into this gambling subgroup.
For more information:
If gambling is negatively affecting your life or others, please visit our First Step to Change website.
–Anjali A. Talcherkar
What do you think? Please use the comment link below to provide feedback on this article.




Mrythorne December 8, 2016
What is the difference between social gamers and non-social gamers, please?
The BASIS December 8, 2016
Thanks for your question. All participants gambled had gambled at some point during the past year. The difference is that social gamers additionally engaged in social gaming, and the rest did not.