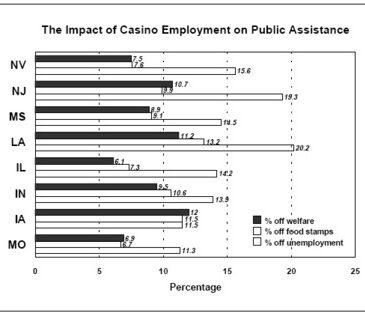
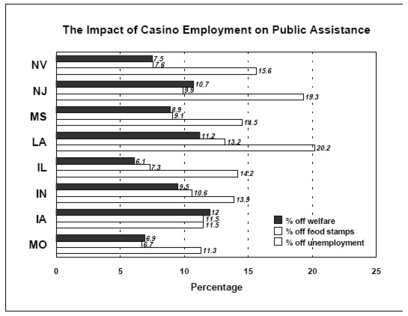
There are an estimated 330,000 employees working in approximately 463 casinos in 10 states within the U.S. as of July, 1997. A recent nationwide survey of casino employees conducted for the American Gaming Association focused on direct employment, job benefits, and community impact of the casino industry. Researchers administered the survey to 54% of the eligible sample, which consisted of casino employees of the industry’s major employers. The response rate was 14%. The majority of the respondents had worked in the gaming industry for five years or less (62%). Results were stratified and adjusted by region due to the disproportionate distribution of employees by region. Nine percent (8.5%) of the respondents reported that they had left welfare as a result of their employment in the gaming industry, 9% of employees stopped receiving food stamps, and 16% of employees reported getting off unemployment. While these individuals credited their shift from public assistance to employment to the gaming industry, it is undeterminable from this study how these casino areas compare to non-casino areas during the same time period. According to Bureau of Labor statistics, the unemployment rate in the U.S. as a whole has decreased fairly consistently from 5.3% (seasonally adjusted percentage) in November 1996 to 4.6% in November 1997. Controlled studies examining economic markers such as unemployment rates by comparing regions with casinos to comparable regions with no casinos will be helpful in further explaining the economic effect of a casino on a community. In addition, higher response rates are essential to guard against the possibility that the 14% of employees who responded are meaningfully different than those that didn’t respond on factors which influence the outcomes of interest.
This public education project is funded, in part, by The Andrews Foundation.